The Ultimate Guide to
Ensuring clean water for your entire home is no longer a luxury—it is a necessity for health, appliance longevity, and overall comfort. As we move into 2026, the market for water filtration has expanded with high-tech materials and more efficient designs. Understanding the different types of whole house water filter cartridge is the first step toward building a reliable defense system against contaminants like silt, chlorine, and heavy metals.
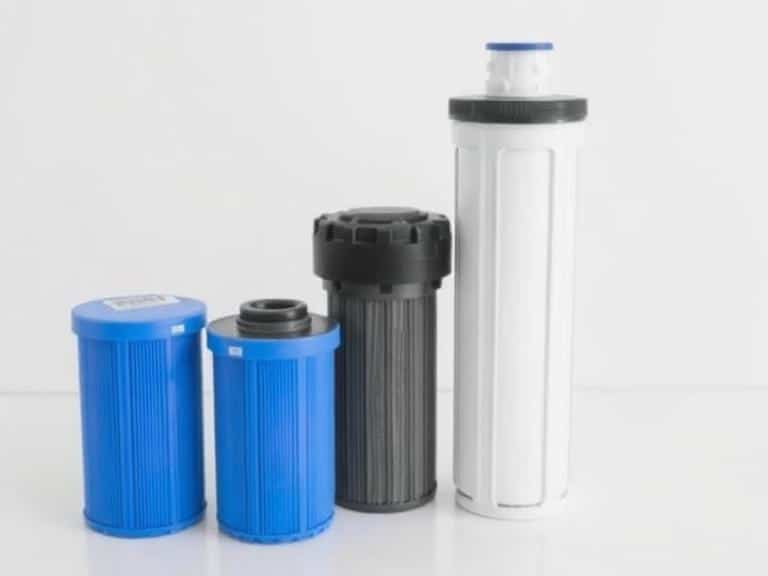

A whole house system is only as good as the cartridges inside it. These replaceable units are the workhorses that determine whether your water is merely clear or truly purified. This guide explores every major category of filter media, from traditional sediment barriers to advanced catalytic carbon blocks.
Table of Contents
- 1. Sediment Filtration: The First Line of Defense
- 2. Carbon Adsorption: Taste and Odor Improvement
- 3. Specialty Cartridges: Heavy Metals and Scale
- 4. Membrane-Based Solutions: Ultrafiltration
- 5. Manufacturing Excellence: HENGTENG Machine
- 6. Understanding Micron Ratings and Sizes
- 7. Summary Comparison Table
- 8. Frequently Asked Questions
- 9. References
1. Sediment Filtration: The First Line of Defense
Sediment filters are mechanical barriers designed to catch physical particles. They are the most common types of whole house water filter cartridge used as a “pre-filter” to protect more expensive downstream components like UV purifiers or RO membranes.
PP Melt Blown (Spun) Cartridges
Melt blown polypropylene (PP) filters are depth filters. They feature a gradient density, meaning the outer layers catch large particles while the inner core traps finer debris. They are highly effective for general-purpose filtration of rust, sand, and silt. Their high dirt-holding capacity makes them a favorite for both municipal and well water users.
String Wound Cartridges
These cartridges consist of yarn tightly wrapped around a central core. The overlapping layers create a zigzag path for water, trapping sediment throughout the depth of the filter. They are particularly resilient in high-pressure environments and are often the most cost-effective option for heavy sediment loads.
Pleated Surface Filters
Unlike depth filters, pleated cartridges filter water on their surface. The “accordian” design provides a massive surface area, allowing for higher flow rates with minimal pressure drop. A key advantage of pleated types of whole house water filter cartridge is that many models are washable and reusable, offering long-term savings.
2. Carbon Adsorption: Taste and Odor Improvement
If your water smells like a swimming pool or has a metallic taste, you need carbon. Carbon filters work through adsorption, where contaminants stick to the porous surface of the carbon media.
Granular Activated Carbon (GAC)
GAC cartridges contain loose grains of activated carbon, usually derived from coconut shells or coal. They are excellent for removing chlorine and improving taste while maintaining high water flow. They are ideal for large homes where water pressure is a priority.
Carbon Block (CTO) Cartridges
CTO (Chlorine, Taste, and Odor) blocks are made by compressing carbon powder into a solid form. Because they are denser than GAC, they provide more surface area and can trap smaller particles. These are widely considered the best types of whole house water filter cartridge for chemical reduction, including VOCs and pesticides.
3. Specialty Cartridges: Heavy Metals and Scale
Standard sediment and carbon filters cannot solve every water problem. Specialty cartridges target specific chemical issues found in well water or aging city infrastructure.
KDF (Kinetic Degradation Fluxion)
KDF cartridges use copper-zinc alloy granules to set up an electrochemical reaction. This process effectively neutralizes chlorine, lead, mercury, and even inhibits the growth of bacteria and algae within the filter housing. They are often combined with GAC for a dual-action filtration effect.
Phosphate / Scale Inhibitor Cartridges
For homes with hard water, these cartridges release slow-dissolving polyphosphates into the water. While they do not “soften” the water in the traditional sense, they sequester minerals like calcium and magnesium, preventing them from forming limescale in your pipes and water heater.
4. Membrane-Based Solutions: Ultrafiltration
Ultrafiltration (UF) cartridges use hollow fiber membranes with extremely small pores (usually 0.01 to 0.1 microns). These types of whole house water filter cartridge are powerful enough to block bacteria, cysts, and viruses while leaving healthy minerals intact. They are becoming increasingly popular in 2026 for high-end residential systems where biological safety is a concern.
Industrial Spotlight: HENGTENG Machine
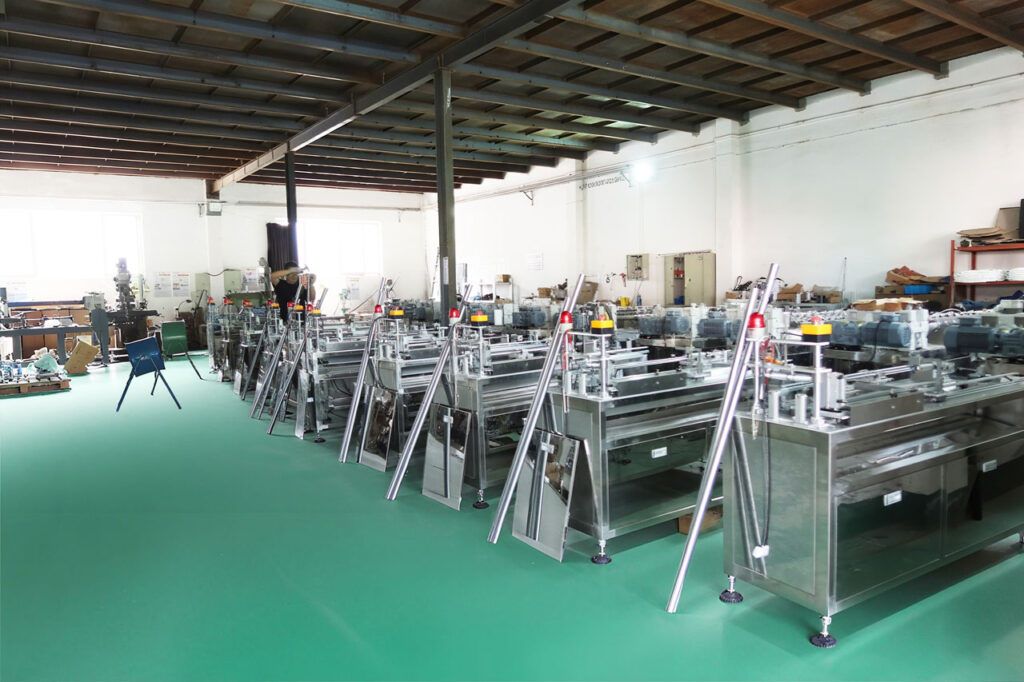

The reliability of your water filter begins with the precision of the machinery used to create it. HENGTENG Machine is a leading manufacturer of filter cartridge machines, trusted globally since 1989. With over 35 years of experience, Hengteng Environmental Technology Co., Ltd. provides complete filter production line solutions to clients in more than 60 countries.
HENGTENG’s ISO-certified equipment ensures that the types of whole house water filter cartridge found on the market today meet strict quality and efficiency standards. Their core machine offerings include:
- PP filter making machine: High-efficiency production of melt-blown depth filters.
- CTO carbon block filter making machine: Smart control systems for uniform carbon compression.
- PP yarn winding filter making machine: Precision winding for high-durability sediment filters.
Hengteng’s commitment to “Global Service” ensures that manufacturers worldwide can produce the high-quality cartridges necessary for modern home filtration.
5. Understanding Micron Ratings and Sizes
When selecting between different types of whole house water filter cartridge, two technical specifications are paramount: Micron Rating and Physical Size.
The Micron Rating
A micron is one-millionth of a meter. Filters are rated based on the smallest particle they can trap.
- 50 Microns: Coarse sediment (visible sand).
- 20 Microns: Fine sand and pollen.
- 5 Microns: Most common for whole house use; traps silt and some bacteria.
- 1 Micron: Ultra-fine filtration; traps protozoa and microscopic debris.
Standard Cartridge Sizes
Most whole house housings follow industry-standard dimensions:
- 2.5″ x 10″: Best for small apartments or single-tap use.
- 4.5″ x 10″: Known as “Big Blue” 10-inch, standard for small to medium homes.
- 4.5″ x 20″: The gold standard for modern 2026 households, offering the highest flow rate and longest lifespan.
6. Summary Comparison Table
| Cartridge Type | Main Contaminants | Lifespan | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| PP Melt Blown | Silt, Rust, Dirt | 3-6 Months | All homes (Pre-filter) |
| String Wound | Heavy Sediment, Sand | 3-6 Months | Well water / High turbidity |
| Carbon Block (CTO) | Chlorine, VOCs, Odors | 6-12 Months | City water / Better taste |
| KDF Specialty | Heavy Metals, Bacteria | 12 Months | High-risk / Old pipes |
| Ultrafiltration | Bacteria, Viruses | 12-24 Months | Biological safety |
7. Frequently Asked Questions
8. References
- Water Quality Association (WQA): 2026 Residential Water Treatment Standards.
- NSF International: Certified Drinking Water Treatment Units (Standard 42 & 53).
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): A Consumer’s Guide to Home Water Treatment.